Care of the Evisceration Injury Patient (Disembowelment)
Posted by RJK / AEMT on 1st Apr 2023
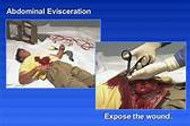
Evisceration is a traumatic injury where the intestines are exposed due to a deep laceration in the abdomen.
People who are not medically trained or in the medical field may panic freak out at such a site during this type of emergency. This type of injury is caused by Any instrument that can impale may inflict a stab wound. Typically, these are narrow, sharp, knife-like implements, but items that can inflict stab wounds range from scissors to coat hangers to animal horns. The given instrument can injure any tissue it traverses, including skin, fascia, solid organ, hollow viscus, blood vessel, nerve, muscle, and bone. As the Intestines protrude it's a traumatic experience for the patient and the responder. It's very important to keep your composure to help the injured patient, it will help them from
First aid for evisceration
1.Check Airway, Breathing and Circulation.
2.Call 911 or your local emergency phone number. Provide information as to the condition of the patient. Be ready to follow instructions.
3.Provide first aid for shock.
4.Control external bleeding.
5.Do not touch or attempt to re-place the organ.
6.Carefully cut away clothing to expose the wound site. Do not attempt to pull away any piece of clothing or article that does not lift off easily.
7.If possible, flex the patient’s uninjured limbs towards the hips and knees to relax abdominal muscles and minimize stress to the wound site.
8.Do not give anything by mouth. Watch out for possible vomiting.
9.Provide reassurance. Stay with the patient.
Cover the exposed organ and wound opening with sterile plastic wrap. If available, a sterile dressing that is soaked in sterile saline solution may be used to cover the protruding organs. Make sure the dressing extends at least two inches beyond the edges of the wound or the exposed organ.
The dressing should be taped in place. It should seal the edges of the organ or wound to create an occlusive dressing. This prevents the internal organ, tissues and organs from drying off. After securing the wet dressing in place, apply a clean towel or a thick dressing pad over the occlusive dressing. This will prevent further heat loss. Use bandage to keep the outermost dressing in place.